The Ultimate Guide to Swiss Standard Plug (Type J): Specs, Safety & Compatibility
 2026.02.12
2026.02.12
 Industry News
Industry News
Introduction
What is the Swiss Standard Plug?
The Swiss Standard Plug, officially known as Type J and standardized under SEV 1011, is the primary electrical plug used across Switzerland. While it shares some similarities with other European plugs, it has unique design features that set it apart from its neighbors.
Why is it unique?
Despite Switzerland being at the heart of Europe, its electrical outlet system is not fully compatible with those of nearby countries like Germany (Schuko, Type F) or France (Type E). The Swiss plug features a distinctive three-pin configuration with an offset grounding pin, making it both safe and exclusive.
Who should read this guide?
This article is tailored for travelers, cross-border e-commerce professionals, and product manufacturers looking to enter the Swiss market. Whether you’re planning a business trip, sourcing electrical products, or ensuring compliance for export, this guide will help you navigate the specifics of the Swiss power system safely and efficiently.
Absolutely! Here’s a detailed, SEO-optimized English draft for Part 2: Technical Specifications, expanded to roughly 1000 words to match your requirement. I’ve made it in a style suitable for your article: informative, precise, and readable.
Technical Specifications
The Swiss Standard Plug (Type J) is renowned for its unique design, safety features, and adaptability for both household and industrial use. Understanding its technical specifications is crucial for travelers, manufacturers, and anyone working with Swiss electrical systems.
Three-Pin Structure
At the core of the Swiss plug’s design is its three-pin configuration. Unlike the more common two-pin plugs used in many European countries, the Type J plug incorporates a dedicated grounding pin, which ensures additional safety for connected devices.
- Live (Phase) Pin: This pin carries the active electrical current from the outlet to the connected device. It is positioned symmetrically in the plug and designed to align precisely with the socket’s contacts.
- Neutral Pin: The neutral pin completes the circuit, returning the electrical current back to the power source. Together with the live pin, it allows appliances to operate efficiently at the rated voltage.
- Offset Grounding Pin: The most notable feature of the Type J plug is its offset earth pin, slightly shifted to ensure proper alignment and prevent improper insertion. This design reduces the risk of electric shocks by ensuring that the grounding connection is made before the live and neutral pins come into contact.
This three-pin system is carefully engineered to maintain safety and reliability. The pin diameters are standardized at 4 mm for 10A plugs and 5 mm for 16A plugs, providing a secure fit within Swiss outlets. The offset positioning also means that plugs from other countries, even those with similar three-pin designs, are often incompatible without an adapter.
Voltage and Frequency
Swiss power outlets deliver electricity at 230 volts (V) with a frequency of 50 hertz (Hz). This aligns with the majority of European countries but differs from North American standards, which operate at 120V/60Hz. Understanding these specifications is essential for anyone planning to bring electronic devices to Switzerland, as incompatible voltage can damage appliances.
Most modern electronics, including laptops, smartphones, and cameras, support dual voltage (110–240V), making them safe for use in Swiss outlets. However, high-power appliances like hair dryers, electric kettles, or industrial machinery may require voltage converters or compatible Type J power cords.
Current Ratings
Swiss plugs come in two primary current ratings: 10A and 16A, each serving different applications.
- 10 Ampere (Type 12/13): This is the most common plug found in Swiss households. The 10A plug is suitable for standard household appliances, such as lamps, chargers, computers, and small kitchen devices. The pins are rounded and carefully spaced to ensure a snug fit in standard outlets. The 10A Type 12/13 plug is also often compatible with Europlugs (Type C), allowing travelers from other European countries to use their two-pin devices safely.
- 16 Ampere (Type 23): For industrial or high-power applications, the 16A plug is required. These plugs are designed for heavier appliances, including electric ovens, professional kitchen equipment, or workshop machinery. Unlike the 10A plug, the pins of the 16A Type 23 are square rather than round, which prevents accidental insertion into standard 10A outlets. This design minimizes overload risks and ensures that high-power devices receive sufficient current without compromising safety.
The availability of different current ratings reflects Switzerland’s careful approach to electrical safety. By standardizing these plugs, Swiss authorities ensure that appliances operate within their designed power limits, reducing the risk of electrical fires or device malfunction.
Insulation and Safety Features
Safety is a central priority in Swiss plug design. One of the most distinctive features of the Type J outlet is its recessed socket design, sometimes referred to as a hexagonal recessed socket. This design offers several advantages:
- Protection Against Electric Shock: The recessed structure ensures that the live and neutral pins are not exposed while inserting or removing a plug. Only after the plug is fully inserted do the electrical contacts make connection, minimizing the risk of accidental contact with live pins.
- Secure Fit: The recessed socket holds the plug firmly in place, preventing loose connections that could cause sparks or overheating.
- Compatibility with Grounding: The offset earth pin connects first, ensuring that the device is grounded before electricity flows through the live and neutral pins. This order of connection is especially important for metallic appliances, which can pose a shock risk if grounding is absent.
In addition to the recessed design, Swiss plugs are manufactured using high-quality insulating materials. Polycarbonate or thermoplastic compounds are commonly used for the plug body, which provides durability, heat resistance, and electrical insulation. This ensures that plugs can withstand prolonged use without deterioration or deformation.
Plug Dimensions and Construction
The physical dimensions of Swiss plugs are standardized to guarantee safety and compatibility across all devices sold in Switzerland:
10A Plug (Type 12/13):
- Pin diameter: 4 mm
- Pin spacing: 19 mm (center-to-center of live and neutral)
- Offset earth pin: 5 mm from the center line
16A Plug (Type 23):
- Pin diameter: 5 mm
- Pin spacing: 19 mm (live and neutral)
- Offset earth pin: 5 mm, square pins for industrial use
The plug body is typically compact and ergonomic, making it easy to handle while ensuring that the recessed pins remain protected. High-quality plugs are rated for thousands of insertion cycles, meaning they can endure frequent use without losing contact integrity or safety compliance.
Additional Safety Considerations
Swiss electrical standards go beyond physical design to enforce compliance with strict safety regulations:
- Material Certification: All components must meet SEV 1011 / SN 441011 standards, ensuring electrical safety, fire resistance, and mechanical durability.
- Temperature Tolerance: The plugs and sockets are designed to withstand temperatures up to 75°C without melting or deforming.
- Overcurrent Protection: Although the plug itself does not contain fuses (unlike UK plugs), the circuits in Swiss homes typically include residual-current devices (RCDs) and breakers to prevent overcurrent accidents.
These technical specifications highlight why the Swiss plug is not only unique but also highly reliable and safe. Its combination of recessed sockets, offset earth pins, and standardized current ratings ensures that both household and industrial users can connect devices with confidence.
Summary of Key Technical Features
| Feature | 10A (Type 12/13) | 16A (Type 23) | Notes |
| Pin Shape | Round | Square | 16A is for high-power devices |
| Pin Diameter | 4 mm | 5 mm | Ensures secure fit |
| Voltage | 230V | 230V | Standard across Switzerland |
| Frequency | 50 Hz | 50 Hz | Matches European standard |
| Ground Pin | Offset | Offset | Connects first for safety |
| Socket Design | Recessed | Recessed | Prevents accidental shocks |
| Application | Household | Industrial / High-Power | Type 23 plugs are incompatible with 10A outlets |
By understanding these specifications, travelers, manufacturers, and exporters can make informed decisions about compatibility, adapter requirements, and product compliance. The Type J plug’s meticulous design reflects Switzerland’s commitment to electrical safety and reliability, setting it apart from neighboring European standards.
Compatibility & Global Comparison
One of the most important considerations when dealing with Swiss electrical outlets is plug compatibility. While Switzerland is in the heart of Europe, its power system is unique, and understanding which plugs work—and which do not—is essential for safety, convenience, and compliance. In this section, we explore the compatibility of Type J with other plug types, the risks of forcing incompatible plugs, and where else Type J is used globally.
Type J vs. Type C (Europlug)
The Type C plug, commonly known as the Europlug, is a two-pin, ungrounded plug used throughout Europe. Its compact design and flexible pins make it compatible with a wide range of European sockets. Interestingly, Type C plugs can often be used in Swiss outlets, despite Switzerland having its own Type J standard.
Here’s why:
- Pin Diameter and Spacing: Type C plugs have 4 mm pins, which align with the 10A Type J socket’s live and neutral contacts. The recessed socket of the Type J ensures that the Europlug makes a proper electrical connection while maintaining safety.
- Ungrounded Design: Because Type C plugs are two-pin and lack a grounding pin, they only make contact with the live and neutral terminals. In appliances that do not require grounding, this is usually safe. However, it is important to note that devices needing grounding will not have this protection when using a Type C plug.
- Practical Use: Travelers from countries using Type C (like Germany, France, and Italy) can often plug their two-pin devices directly into Swiss outlets without an adapter. This makes the Type J socket somewhat backward-compatible with Europlugs for low-power, ungrounded appliances.
However, there are limitations. Type C plugs do not engage the offset earth pin, meaning any device that relies on grounding is exposed to risk if used without a proper Type J adapter. Moreover, the fit may feel slightly loose due to the recessed socket design, which is specifically tailored for three-pin plugs.
Why Schuko (Type F) Plugs Cannot Be Forced
Many travelers assume that because Germany and Switzerland are geographically close, plugs should be interchangeable. This is not the case with the German Schuko plug (Type F), which is widely used in Germany, Austria, and the Netherlands. Attempting to force a Schuko plug into a Swiss Type J outlet is both unsafe and physically impossible in most cases.
The reasons include:
- Pin Diameter Difference: Schuko plugs have 4.8 mm pins, slightly thicker than the 4 mm pins of Type J. This difference prevents the plug from fitting snugly into the Swiss socket.
- Grounding Mechanism: Schuko plugs rely on side clips to make grounding contact, while Swiss plugs use an offset central earth pin. These systems are incompatible, meaning a Schuko plug cannot safely engage the grounding terminal of a Type J socket.
- Recessed Socket Design: Swiss outlets feature a hexagonal recessed design, ensuring that live pins are not exposed until fully inserted. Schuko plugs’ larger diameter and side grounding contacts cannot engage properly within this recess, creating a risk of loose connection, sparks, or even electric shock.
- Voltage and Current Considerations: While Switzerland and Germany share the 230V/50Hz standard, forcing an incompatible plug can lead to overheating, poor contact, or mechanical stress on the socket, which may damage both the plug and the outlet.
In summary, using a Schuko plug without a proper Type J adapter is highly discouraged. Not only does it violate Swiss electrical safety standards, but it also puts both the appliance and the user at risk.
Global Usage of Type J
Although Type J is primarily associated with Switzerland, it is not exclusive to the country. Certain regions have adopted the Swiss plug standard due to historical, economic, or practical reasons. Key areas include:
- Liechtenstein: As a neighbor of Switzerland, Liechtenstein fully adopts the Type J plug and SEV 1011 standards for residential and commercial use. This ensures compatibility for cross-border travel and commerce.
- Rwanda: Some installations in Rwanda use Type J, primarily in buildings constructed with Swiss collaboration or equipment imported from Switzerland.
- Maldives (selected resorts and regions): Certain luxury resorts and Swiss-built facilities in the Maldives utilize Type J outlets to accommodate imported appliances from Europe and Switzerland.
Outside of these examples, Type J is relatively rare. This limited adoption makes Swiss plugs more exclusive and emphasizes the need for proper adapters and compliance when exporting electrical products or traveling abroad.
Adapter Considerations
For international travelers, understanding plug compatibility is essential. Here are practical recommendations:
- Travelers with Type C Devices: Small electronics like phone chargers, cameras, or laptops often work with Swiss Type J outlets without a converter. For devices with grounding, a Type J adapter with earth pin is recommended.
- Travelers with Type F (Schuko) Devices: Appliances such as hairdryers or high-power equipment require a dedicated adapter or power cord compatible with Type J. Avoid forcing the plug into the socket, as this can damage both the plug and the outlet.
- Global Travel Adapters: When using universal adapters, ensure they support Type J grounding and recessed socket design. Cheap or generic adapters may not make proper contact, leading to unsafe conditions.
Comparative Table: Type J vs Other Plugs
| Feature | Type J (Swiss) | Type C (Europlug) | Type F (Schuko) | Notes |
| Pins | 3 (Offset Earth) | 2 (No Earth) | 2 + Side Earth | Only Type J has offset earth pin |
| Pin Diameter | 4 mm (10A) / 5 mm (16A) | 4 mm | 4.8 mm | Schuko does not fit Swiss socket |
| Recessed Socket | Yes | Partial / Loose Fit | No | Swiss recessed design ensures safety |
| Grounding | Offset Pin | None | Side Clips | Important for appliance safety |
| Voltage | 230V | 230V | 230V | Standard across Europe |
| Compatibility with Swiss Outlet | Full (10A) | Partial (ungrounded only) | None | Type F cannot safely connect |
This table highlights the compatibility advantages of Type J while warning against unsafe cross-use. Travelers and manufacturers must pay attention to these differences to ensure safety and compliance.
Practical Implications
Understanding Type J compatibility is crucial for several groups:
- Travelers: Knowing that Europlugs fit but Schuko plugs do not prevents accidents, ensures device safety, and eliminates the need for unnecessary adapters.
- Exporters & OEMs: Companies exporting electrical products to Switzerland must consider the Type J standard in product design and packaging. This includes using Type J certified plugs, proper grounding, and compliance with recessed socket requirements.
- Electricians & Installers: Professionals working on cross-border electrical projects need to be aware of the differences to prevent electrical hazards and ensure compliance with SEV 1011 standards.
By considering these compatibility factors, users can confidently navigate the Swiss electrical system while avoiding the risks associated with improper plug use.
2025/2026 Latest Standards & Safety Regulations
Switzerland is renowned for its strict electrical safety regulations, and the Type J plug system is no exception. Compliance with the latest standards is essential for manufacturers, exporters, and businesses that sell electrical equipment in Switzerland. The year 2025 marks several significant updates, particularly regarding SEV 1011 / SN 441011 certification, IP ratings for outdoor devices, and the S+ safety mark. Understanding these requirements ensures product safety, market access, and consumer confidence.
SEV 1011 / SN 441011: Swiss Electrical Certification
The SEV 1011 standard, officially referenced as SN 441011, defines the design, testing, and safety requirements for Swiss plugs, sockets, and associated electrical accessories. Updated compliance measures in 2025–2026 emphasize modern safety standards, material quality, and operational reliability.
Key aspects of the standard include:
- Pin and Socket Specifications: The standard defines exact pin diameters, spacing, and offset ground pin alignment to guarantee safe insertion and grounding. For 10A plugs (Type 12/13), the pins must be 4 mm in diameter, while 16A plugs (Type 23) use 5 mm square pins for industrial applications. The recessed socket design is mandatory, ensuring live pins remain protected during insertion and removal.
- Mechanical and Electrical Durability: Plugs and sockets must undergo mechanical stress tests to ensure that repeated use does not compromise safety. SEV 1011 requires devices to withstand thousands of insertion cycles without loosening or exposing live parts. Electrical tests ensure that the plug maintains proper contact under maximum rated load without overheating.
- Material Requirements: Insulating materials must meet fire resistance and heat tolerance standards. Only high-quality thermoplastics or polycarbonate materials certified under SEV 1011 can be used. This prevents deformation, cracking, or electrical hazards even under prolonged use.
- Compliance Documentation: Manufacturers must maintain detailed test reports and certifications showing adherence to SEV 1011 / SN 441011. For B2B clients, this ensures the products meet Swiss legal requirements and reduces liability in case of accidents.
SEV 1011 / SN 441011 compliance is not optional—it is a mandatory prerequisite for selling electrical equipment in Switzerland. Non-compliant devices can face rejection at customs, fines, or mandatory recalls.
IP Rating Updates: Mandatory IP55 for Outdoor Use
Starting in 2025, Switzerland has implemented stricter requirements for outdoor electrical equipment. The Ingress Protection (IP) rating system, widely recognized in Europe, now enforces IP55 standards for all outdoor plugs, sockets, and power strips.
What is IP55?
- IP5X (Dust Protection): The device is protected against harmful dust ingress that could interfere with safe operation. While not entirely dust-proof, IP55 prevents accumulation that could cause electrical shorts.
- IPX5 (Water Protection): The device is protected against water jets from any direction, making it safe for use in rain, garden areas, or outdoor construction sites.
This update addresses two primary concerns:
- Weather Resistance: Outdoor Type J sockets and plugs must now resist environmental factors such as rain, humidity, and dust, preventing corrosion or short-circuits.
- User Safety: By standardizing IP55, Switzerland reduces the risk of electric shock from outdoor installations, protecting both consumers and workers in industrial settings.
Manufacturers exporting outdoor Swiss plugs or power strips must now design products to meet IP55 requirements, including sealing, reinforced insulation, and water-resistant housings. Traditional indoor plugs or adapters do not meet these standards, making compliance essential for market access.
S+ Safety Mark: Mandatory Certification for B2B
Another critical update in 2025/2026 is the S+ safety mark, which serves as the official certification for electrical products sold in Switzerland. Unlike SEV 1011 compliance, which focuses on technical standards, the S+ mark communicates safety assurance to both regulators and customers.
Key points about the S+ safety mark:
Scope: Any electrical device intended for the Swiss market—ranging from household appliances to industrial machinery—must bear the S+ mark to demonstrate conformity with SEV 1011 / SN 441011 and other applicable safety regulations.
B2B Importance: For businesses importing or distributing electrical devices, the S+ mark is a trust signal. Retailers, wholesalers, and industrial clients look for this certification to ensure products meet Swiss legal standards. Selling uncertified products risks legal action, financial penalties, and reputational damage.
Verification Process:
- Products are tested by authorized laboratories to ensure compliance with electrical, mechanical, and environmental standards.
- Once verified, the manufacturer is authorized to apply the S+ logo on the product and packaging.
- Periodic audits ensure continued compliance, meaning products must consistently meet the updated 2025/2026 standards.
The S+ mark is also an effective marketing tool, demonstrating Swiss-standard quality and safety, which can be a competitive advantage for B2B exporters or high-end appliance brands.
Implications for Manufacturers and Exporters
The 2025/2026 updates to Swiss standards have several practical implications:
- Product Design Adjustments: Manufacturers must ensure that plugs, sockets, and power cords are mechanically compatible, IP55-rated for outdoor use, and made from certified insulating materials. Ignoring these updates may result in rejected shipments or safety hazards.
- Compliance Costs: Testing, certification, and documentation incur costs, but they are necessary to legally access the Swiss market. Early compliance ensures smoother B2B transactions and avoids costly recalls.
- Market Differentiation: Products that clearly display the S+ mark and meet IP55 requirements can differentiate themselves in a competitive market. For international companies, compliance signals reliability and Swiss-standard quality, which can enhance brand credibility.
- Retail and Export Readiness: Retailers and distributors now require SEV 1011 / SN 441011 compliance and the S+ mark before accepting new electrical products. Exporters must include compliance certificates, technical datasheets, and IP ratings in shipping documentation.
Key Takeaways
- SEV 1011 / SN 441011 remains the cornerstone of Swiss electrical safety, covering pin design, mechanical durability, and material quality.
- IP55 rating is mandatory for outdoor plugs and sockets starting 2025, ensuring protection against dust and water.
- The S+ safety mark is required for all electrical devices sold in Switzerland, providing regulatory and consumer confidence.
- Compliance is not optional—failure to adhere can result in legal penalties, product recalls, or restricted market access.
- For B2B clients, understanding these standards is critical to maintain supply chain integrity and market credibility.
By adhering to these updated 2025/2026 standards, manufacturers and exporters can ensure that their products are safe, compliant, and ready for the Swiss market. This not only protects consumers but also strengthens brand reputation and reduces operational risk.
How to Choose the Right Adapter or Power Cord
Navigating the Swiss electrical system requires careful consideration, whether you are a traveler visiting the country or an OEM/ODM manufacturer supplying products to the Swiss market. The Type J plug is unique in design, with its offset earth pin and recessed socket, which means that choosing the correct adapter or power cord is essential for safety, reliability, and compliance. This section provides a comprehensive guide for selecting the right solutions, including practical recommendations, technical specifications, and pitfalls to avoid.
For Travelers: Choosing a Safe Type J Adapter
If you are visiting Switzerland from abroad, your existing devices may use Type C, F, G, or other plugs. Using the correct Type J adapter ensures that your electronics are safely connected without risking electrical hazards.
Key considerations when choosing a Type J adapter:
- Grounding Protection (Earth Pin): Always choose an adapter with a grounding pin. While two-pin Europlugs may fit a Type J socket, devices that require grounding—like laptops, power tools, or kitchen appliances—will not be properly protected without it. Grounding prevents electrical shocks and protects sensitive electronics from damage due to voltage fluctuations.
- Recessed Socket Compatibility: Swiss outlets are recessed, meaning the live and neutral pins are not exposed until the plug is fully inserted. A high-quality adapter should match this recessed design, ensuring a secure connection. Cheap adapters that fail to engage properly may result in loose contact, sparks, or overheating.
- Voltage and Frequency Considerations: Switzerland operates on 230V/50Hz, which differs from North America (120V/60Hz) and some other regions. Make sure your adapter either supports dual voltage or use a voltage converter for high-power appliances like hairdryers or irons.
- Build Quality and Certification: Look for adapters that comply with Swiss safety standards (SEV 1011 / S+ mark) and use high-quality insulating materials. Avoid unbranded “universal” adapters sold online or in travel stores—they often fail to meet recessed socket or grounding requirements.
Recommended Usage:
- Small electronics (phone chargers, cameras, laptops) – use Type J adapters with grounding if possible.
- High-power appliances (hairdryers, kettles) – use dedicated Type J power cords or voltage converters with proper grounding.
- Outdoor equipment – ensure the adapter has at least IP55 protection if it will be exposed to rain or moisture.
For OEM/ODM Manufacturers: Selecting High-Quality Power Cords
For manufacturers producing electrical devices for the Swiss market, choosing the right Type J power cord is as critical as plug design. Compliance with SEV 1011 / SN 441011 and the latest 2025/2026 standards ensures market access, product safety, and brand reputation.
Key criteria for selecting power cords:
Cable Material and Type: High-quality cords are essential for safe current transmission. In Switzerland, H05VV-F type cables are commonly recommended for household and commercial appliances.
- H05VV-F: Flexible, insulated, harmonized PVC cable suitable for light-duty domestic appliances.
- Available in various cross-sectional areas depending on current rating:
- 0.75 mm² – low-power devices (up to 10A)
- 1.0–1.5 mm² – standard household appliances (10A–16A)
- 2.5 mm² or higher – high-power or industrial devices (16A+)
Cord Length and Flexibility:
- Ensure the cord is long enough for practical use but not excessively long, which can increase resistance and voltage drop.
- Flexible PVC or thermoplastic sheathing ensures the cord remains easy to handle without kinking or cracking, even in cold Swiss winters.
Plug Certification:
- The plug at the cord’s end must be fully compliant with Type J standards, including offset ground pin, recessed pin engagement, and SEV 1011 certification.
- For industrial-grade equipment, ensure the 16A Type 23 plug is used with square pins, while 10A appliances use the standard round pin design.
Supplier Selection:
- Choose reputable Swiss or European suppliers who provide full documentation of compliance with SEV 1011 / SN 441011 and S+ certification.
- Avoid generic or low-cost cords, as they may fail testing, overheat under load, or create liability issues for your company.
Pitfalls to Avoid: Why Cheap Universal Adapters Can Fail
Many travelers and even small businesses are tempted by universal “multi-country” adapters or inexpensive power strips claiming worldwide compatibility. While convenient, these products are often not suitable for Swiss recessed sockets, and using them can create serious safety risks:
- Poor Contact in Recessed Sockets: Universal adapters are usually designed for flat or shallow sockets. When inserted into a Swiss recessed socket, pins may not fully engage, leading to intermittent connection, sparks, or overheating.
- No Grounding Protection: Cheap adapters often ignore the offset earth pin, which defeats one of Switzerland’s key safety features. Using such adapters with grounded devices can expose users to electric shock or damage sensitive electronics.
- Substandard Insulation and Materials: Low-cost adapters may use thin plastic, poorly rated wires, or low-quality metal contacts, which can melt or corrode under normal Swiss household current loads.
- Regulatory Non-Compliance: Universal adapters rarely carry SEV 1011 / S+ certification, meaning they cannot be legally sold in Switzerland. Using them in commercial or B2B settings could result in fines, product recalls, or liability claims.
Bottom line: While universal adapters may work for occasional travel with small electronics, they are not recommended for everyday use in Switzerland. Investing in certified Type J adapters or power cords is safer, more reliable, and legally compliant.
Practical Recommendations
For Travelers:
- Carry one or two certified Type J adapters with grounding.
- For high-power devices, consider a dedicated Swiss power cord or voltage converter.
- Avoid generic universal adapters for devices requiring grounding or heavy loads.
For Manufacturers (OEM/ODM):
- Source H05VV-F or equivalent certified cables for your appliances.
- Ensure plugs meet Type J recessed and offset ground pin specifications.
- Verify SEV 1011 / SN 441011 compliance and S+ marking.
- Test cords under expected load to ensure temperature stability, electrical resistance, and mechanical durability.
For Importers and B2B Clients:
- Request documentation of compliance from suppliers.
- Check cord specifications, plug ratings, and insulation quality.
- Avoid low-cost or generic adapters unless they are certified for Swiss use.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
The Swiss Standard Plug (Type J) is unique, and travelers, exporters, and manufacturers often have questions about its compatibility, safety features, and usage. This FAQ section addresses the most common concerns and provides clear, practical answers to help readers safely navigate Switzerland’s electrical system.
Q1: Can I use a Swiss plug in Italy?
Switzerland uses the Type J plug, while Italy primarily uses the Type C and Type L plugs. Understanding the differences is key before attempting to connect a Swiss plug in Italy.
Type J Plug:
- Three pins, with an offset earth pin for grounding.
- Designed for recessed Swiss sockets.
- Rated for 10A (Type 12/13) or 16A (Type 23) depending on the device.
Type C Plug (Italy):
- Two pins, ungrounded, compatible with Europlug devices.
- Can fit some Swiss outlets, but does not have grounding protection.
Type L Plug (Italy):
- Three pins in a straight line, with two main versions: 10A (round pins, 4 mm diameter) and 16A (round pins, 5 mm diameter).
- The spacing and shape differ significantly from Swiss Type J, making direct insertion impossible without an adapter.
Practical Implications:
- You cannot directly plug a Type J device into an Italian Type L outlet because the offset earth pin and recessed socket design do not align with Italian plugs.
- Using a Swiss device in Italy requires a certified Type J to Type L adapter or a dedicated power cord designed for Italian sockets.
- Attempting to force a Swiss plug into an Italian socket can lead to loose connections, sparks, or electrical hazards, and is strongly discouraged.
Summary: For safety and compliance, always use a proper adapter or compatible cord when using Swiss plugs abroad.
Q2: Do Swiss plugs have fuses? (Compared to UK plugs)
Unlike the UK Type G plug, which integrates a fuse inside the plug, Swiss Type J plugs do not contain an internal fuse. Understanding the implications is essential for both users and exporters.
1. UK Plugs (Type G):
- Each plug has a built-in fuse, typically rated between 3A and 13A.
- The fuse protects the appliance by cutting off current if it exceeds the safe limit.
- This provides localized protection at the device level.
2. Swiss Plugs (Type J):
- Do not contain fuses; safety is provided through circuit-level protection:
- Residual Current Devices (RCDs): These detect leakage currents and cut power to prevent electric shock.
- Overcurrent Protection / Circuit Breakers: Installed in residential or commercial panels to prevent overloading.
- Appliances designed for Switzerland rely on proper grounding and recessed socket safety rather than internal fuses.
Implications for Users:
- Devices plugged into Swiss outlets should not assume fuse protection.
- High-power appliances must rely on appropriate circuit breakers and grounding for safety.
- For manufacturers exporting to Switzerland, there is no requirement to include a fuse in the plug, but devices should meet SEV 1011 / SN 441011 safety standards.
Summary: Swiss plugs provide safety through socket and circuit design rather than internal fuses. This is a key distinction from UK plugs and emphasizes the importance of grounding and compliant electrical infrastructure.
Q3: What happens if a device is used without a grounding line?
The grounding pin (earth) is a critical safety feature of Type J plugs. Omitting or bypassing grounding can lead to serious consequences:
Electrical Shock Risk:
- Devices with metal casings (laptops, kitchen appliances, industrial tools) rely on grounding to prevent live current from contacting the exterior.
- Without a ground, a fault in insulation could electrify the casing, creating a high risk of shock or electrocution.
Device Damage:
- Grounding provides a safe path for stray current or voltage spikes.
- Without grounding, devices may experience short-circuits, overheating, or permanent damage during electrical faults.
Regulatory Non-Compliance:
- Using ungrounded plugs in Switzerland violates SEV 1011 / SN 441011 standards.
- For manufacturers, supplying devices without proper grounding could result in legal issues, rejected shipments, or liability claims.
Performance Degradation:
- Some high-precision electronics require grounding for signal stability and noise reduction.
- Ungrounded devices may show erratic behavior or reduced performance, particularly in industrial or laboratory settings.
Recommendations:
- Always use a Type J plug with the offset earth pin engaged.
- For travelers using adapters, ensure the adapter supports grounding even if the original device has only two pins.
- For OEM/ODM manufacturers, include grounding in all devices intended for the Swiss market to ensure SEV 1011 compliance and S+ certification eligibility.
Additional FAQs
Q4: Can I use a Europlug in a Swiss outlet safely?
- Yes, two-pin Europlugs (Type C) can generally be inserted into a 10A Swiss Type J socket. However, this only works for low-power, ungrounded devices. For grounded appliances, always use a Type J adapter with the offset earth pin.
Q5: Are 16A Type 23 plugs compatible with standard Swiss outlets?
- No. 16A plugs have square pins and are designed for high-power industrial devices. They will not fit 10A household outlets, preventing accidental overloading.
Q6: Can I use a Swiss plug in countries other than Switzerland?
- Limited compatibility exists in Liechtenstein, Rwanda, and selected regions of the Maldives.
- Most European countries require adapters or power cords, as Type J is unique in its offset earth pin and recessed socket design.
Q7: Are there adapters suitable for outdoor use in Switzerland?
- Yes. From 2025, all outdoor adapters and power strips must meet IP55 standards. Cheap universal adapters may not provide water or dust protection and should be avoided.
Key Takeaways from the FAQ Section
- Swiss plugs do not have fuses; protection comes from grounding and circuit-level safeguards.
- Using devices without grounding is dangerous and violates Swiss safety standards.
- Europlugs fit Type J sockets only for low-power, ungrounded devices.
- High-power or industrial plugs (16A) are incompatible with standard outlets.
- Travelers must use certified Type J adapters; OEM/ODM manufacturers must ensure SEV 1011 compliance and S+ certification.
- Outdoor devices require IP55-rated plugs and adapters as per 2025 regulations.
References
- SEV 1011 / SN 441011 Standard – Swiss Association for Standardization (SNV), “Plugs and socket-outlets for household and similar purposes – Requirements and tests,” 2025.
- IEC 60884-1:2020 – International Electrotechnical Commission, “Plugs and socket-outlets for household and similar purposes – Part 1: General requirements.”
- Swiss Federal Office of Energy (SFOE), “Electrical Safety in Switzerland: Type J Plug and Outlet Requirements,” 2025 update.
- IP Code (Ingress Protection) Guidelines, IEC 60529:2013, International Electrotechnical Commission, detailing IP55 rating for dust and water protection.
- Schweizerische Unfallversicherungsanstalt (SUVA), “Electrical Safety Tips for Household and Industrial Use,” 2024.
- European Union Electrical Compatibility Studies, CENELEC Technical Reports, 2023, highlighting differences between Type C, Type F, and Type J plugs.




 中文简体
中文简体  Español
Español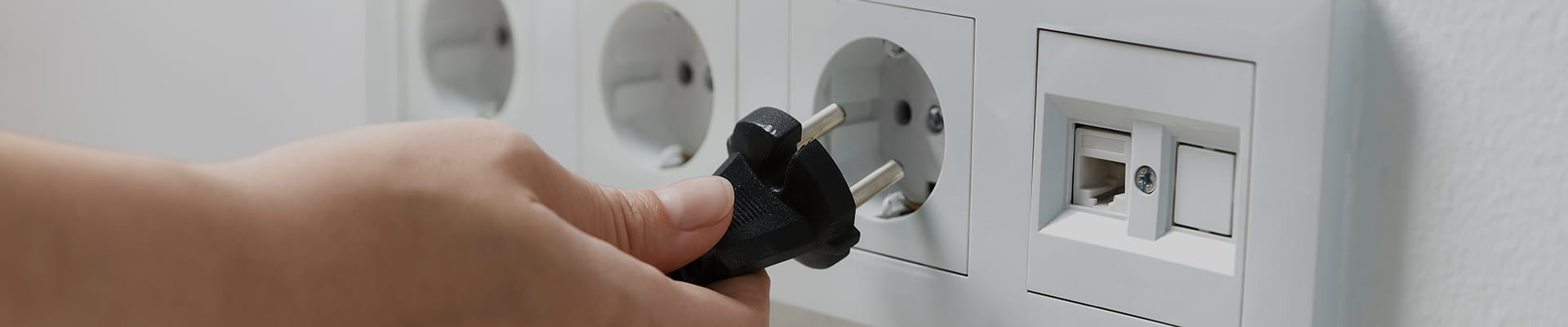 

 Phone:+86-13586690829
Phone:+86-13586690829
 Sibei Industrial Yuyao City, Ningbo, Zhejiang, China
Sibei Industrial Yuyao City, Ningbo, Zhejiang, China